Perspective:
For centuries, global power dynamics have been dominated by Western countries, with the United States and Europe at the forefront. However, the emergence of new global powers such as China and India is reshaping the global landscape. Understanding this shift is crucial for comprehending the future of global politics, economy, and society.
Historical Context of Global Power Dynamics:
The Western dominance of global power can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century. This period marked significant advancements in technology, industry, and military power, primarily in Western Europe and later in the United States. Key historical events solidified this dominance, including:
- Colonialism: European countries expanded their empires, controlling vast territories in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- World Wars: The aftermath of World War I and World War II saw the United States emerge as a superpower, with Europe recovering from extensive damage.
- Cold War: The ideological and geopolitical struggle between the United States and the Soviet Union further entrenched Western influence, with the eventual collapse of the Soviet Union solidifying U.S. dominance.

The Rise of China:
China’s transformation over the past few decades has been nothing short of remarkable.
- Economic Growth: Since initiating economic reforms in 1978, China has experienced unprecedented growth, becoming the world’s second-largest economy. The country’s GDP has grown at an average rate of nearly 10% annually, lifting hundreds of millions out of poverty and transforming China into a global manufacturing hub.
- Military Expansion: Alongside economic growth, China has significantly modernized and expanded its military capabilities. The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has become one of the world’s most formidable forces, with advancements in naval, missile, and cyber capabilities.
- Political Influence: China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) aims to enhance global trade connectivity through infrastructure investments across Asia, Africa, and Europe. This initiative has increased China’s geopolitical influence, drawing countries into its economic orbit.
- Technological Advancements: China leads in several technology sectors, including artificial intelligence (AI), 5G telecommunications, and quantum computing. Companies like Huawei and Alibaba are at the forefront of innovation, challenging Western tech giants.

The Rise of India:
India’s rise on the global stage is equally significant.
- Economic Development: India is one of the fastest-growing major economies, with a burgeoning middle class and a growing influence in global markets. The country has become a major player in information technology, pharmaceuticals, and services.
- Demographic Advantage: With a population of over 1.4 billion, India has a young workforce that presents immense economic potential. This demographic dividend is expected to drive economic growth for decades.
- Military Modernization: India has steadily enhanced its defense capabilities, investing in advanced technology and expanding its military presence. The country’s strategic location in the Indian Ocean region adds to its geopolitical importance.
- Political and Diplomatic Influence: India plays a crucial role in international organizations such as the United Nations, G20, and BRICS. Strategic partnerships with countries like the United States, Japan, and Australia further bolster its global standing.
Challenges to Western Dominance:
The rise of China and India presents several challenges to traditional Western dominance.
- Economic Competition: The economic rise of these emerging powers has increased competition in global markets, impacting trade balances and investment flows. Western economies must adapt to this new reality, fostering innovation and competitiveness.
- Shifts in Trade and Investment: The global trade landscape is shifting, with China and India becoming major trade partners for many countries. The BRI and other regional initiatives are reshaping trade routes and investment patterns.
- Technological Rivalry: Emerging economies are competing in cutting-edge technologies, challenging Western technological supremacy. The race for leadership in AI, 5G, and renewable energy is intensifying.
- Soft Power Dynamics: China and India are expanding their cultural influence through initiatives like Confucius Institutes and cultural diplomacy. These efforts are reshaping global perceptions and enhancing their soft power.
Regional and Global Implications:
The shifting power dynamics have profound regional and global implications.
- Impact on Asia: The rise of China and India is altering the regional power balance in Asia. Relationships with neighboring countries are evolving, with some aligning closely with these emerging powers, while others seek to counterbalance their influence.
- Global Alliances: Shifts in alliances and partnerships are evident, with groupings like BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) and the Quad (United States, Japan, India, Australia) playing significant roles in shaping global geopolitics.
- Influence on Global Governance: Emerging powers are advocating for changes in international organizations and rule-making processes. Calls for reform in institutions like the United Nations Security Council reflect the desire for a more multipolar world order.
Case Studies:
Examining specific geopolitical scenarios helps illustrate the broader trends.
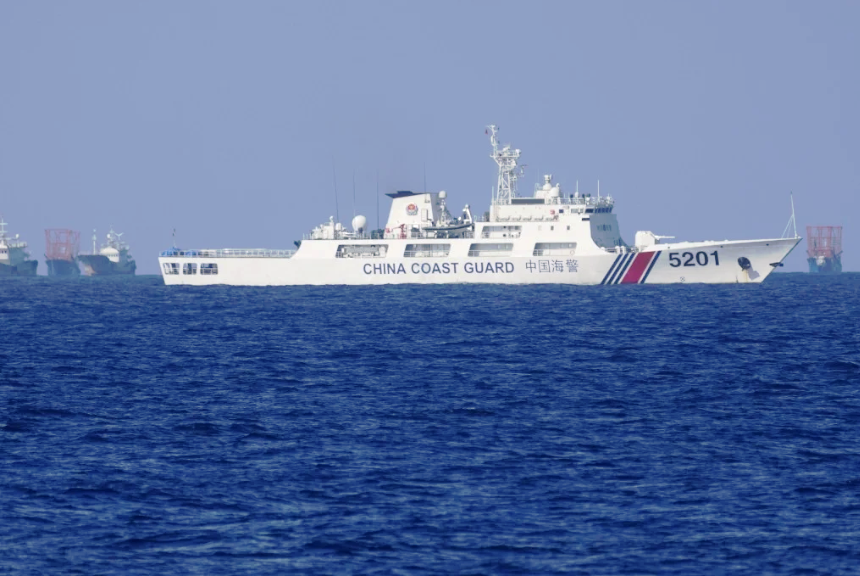
# South China Sea:
China’s territorial claims and military buildup in the South China Sea have led to geopolitical tensions and territorial disputes with neighboring countries. This region remains a flashpoint for potential conflicts.

# Indo-Pacific Strategy:
India’s strategic initiatives in the Indo-Pacific region aim to enhance security and economic cooperation. Partnerships with countries like the United States, Japan, and Australia are central to this strategy.
# Trade Wars:
The US-China trade war exemplifies the economic conflicts arising from shifting power dynamics. Tariffs, trade restrictions, and technological competition have far-reaching implications for global trade.

Future Outlook:
Predicting the future of global power dynamics involves considering various scenarios.
Cooperation and Conflict: Potential areas of cooperation include combating climate change, addressing global health challenges, and promoting sustainable development. However, conflicts may arise over trade, territorial disputes, and technological dominance.
Role of Emerging Technologies: Emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and renewable energy will play critical roles in shaping future power dynamics. Leadership in these areas will determine global influence.
Conclusion:
The shifting global power dynamics mark a significant departure from the historical dominance of Western countries. Understanding these changes is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. By staying informed and engaged with global developments, we can navigate this complex landscape and work towards a more balanced and multipolar world order.
References:
- World Bank Data
- International Monetary Fund (IMF) Reports
- United Nations Publications
- Research Papers on Geopolitics
- News Articles and Expert Analyses

